When to step-up your Google Pay transactions as a PSP
Posted by Dominik Mengelt, Developer Relations Engineer, Google Pay and Nick Alteen, Technical Writer, Engineering, Wallet What is step-up authentication? When processing payments, step-up authentication (or simply “step-up”) is the practice of requiring additional authentication measures based on user activity and certain risk signals. For example, redirecting the user to 3D Secure to authenticate a transaction. This can help to reduce potential fraud and chargebacks. The following graphic shows the high-level flow of a transaction to determine what's to be done if step-up is needed. Figure 1: Trigger your Risk Engine before sending the transaction to authorization if step-up is needed It depends! When making a transaction, the Google Pay API response will return one of the following: An authenticated payload that can be processed without any further step-up or challenge. For example, when a user adds a payment card to Google Wallet. In this case, the user has already completed


Posted by Dominik Mengelt, Developer Relations Engineer, Google Pay and Nick Alteen, Technical Writer, Engineering, Wallet
What is step-up authentication?
When processing payments, step-up authentication (or simply “step-up”) is the practice of requiring additional authentication measures based on user activity and certain risk signals. For example, redirecting the user to 3D Secure to authenticate a transaction. This can help to reduce potential fraud and chargebacks. The following graphic shows the high-level flow of a transaction to determine what's to be done if step-up is needed.
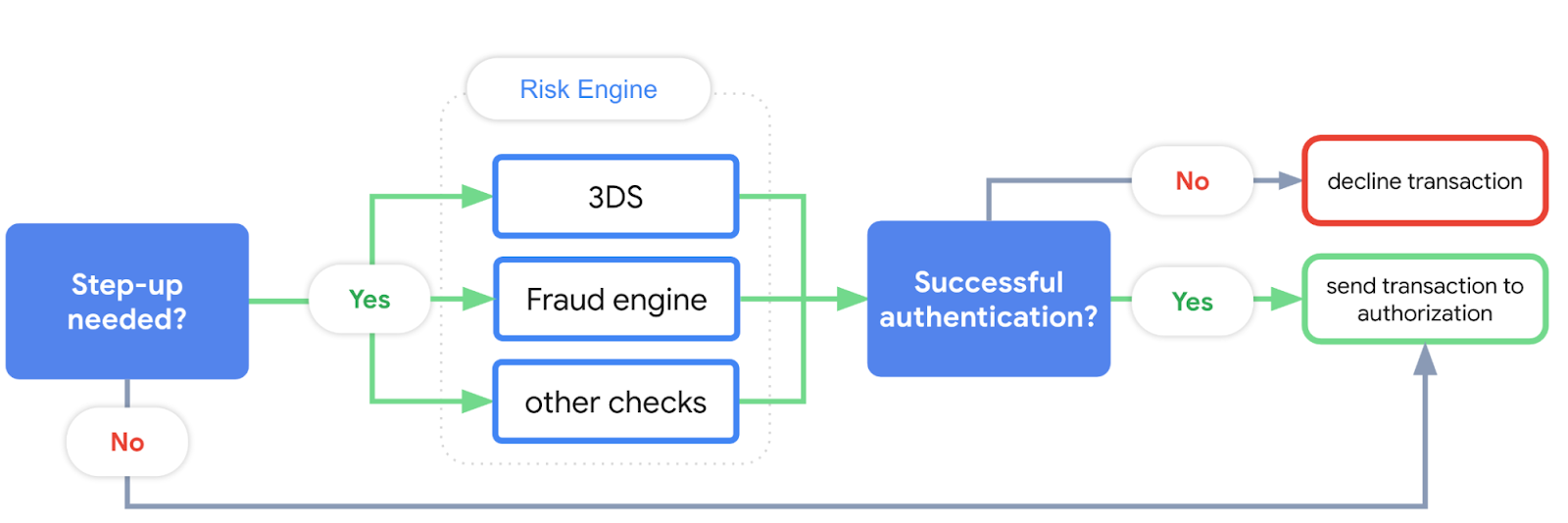 |
| Figure 1: Trigger your Risk Engine before sending the transaction to authorization if step-up is needed |
It depends! When making a transaction, the Google Pay API response will return one of the following:
- An authenticated payload that can be processed without any further step-up or challenge. For example, when a user adds a payment card to Google Wallet. In this case, the user has already completed identity verification with their issuing bank.
- A primary account number (PAN) that requires additional authentication measures, such as 3D Secure. For example, a user making a purchase with a payment card previously stored through Chrome Autofill.
You can use the allowedAuthMethods parameter to indicate which authentication methods you want to support for Google Pay transactions:
"allowedAuthMethods": [ |
PAN_ONLY card (a card not tokenized, not enabled for contactless) from the payment sheet during checkout, step-up is needed. Let's have a look at two concrete scenarios:CRYPTOGRAM_3DS authentication method.On the other hand, the sheet in the second scenario shows a generic card network icon. This indicates a PAN_ONLY authentication method and therefore needs step-up.
PAN_ONLY vs. CRYPTOGRAM_3DS
Whether or not you decide to accept both forms of payments is your decision. For CRYPTOGRAM_3DS, the Google Pay API additionally returns a cryptogram and, depending on the network, an eciIndicator. Make sure to use those properties when continuing with authorization.
PAN_ONLY | This authentication method is associated with payment cards from a user’s Google Account. Returned payment data includes the PAN with the expiration month and year. |
CRYPTOGRAM_3DS | This authentication method is associated with cards stored as Android device tokens provided by the issuers. Returned payment data includes a cryptogram generated on the device. |
When should you step-up Google Pay transactions?
When calling the loadPaymentData method, the Google Pay API will return an encrypted payment token (paymentData.paymentMethodData.tokenizationData.token). After decryption, the paymentMethodDetails object contains a property, assuranceDetails, which has the following format:
"assuranceDetails": { |
Depending on the values of
cardHolderAuthenticated and accountVerified, step-up authentication may be required. The following table indicates the possible scenarios and when Google recommends step-up authentication for a transaction:cardHolderAuthenticated | accountVerified | Step-up needed |
true | true | No |
false | true | Yes |
Step-up can be skipped only when both cardHolderAuthenticated and accountVerified return true.
Next steps
If you are not using assuranceDetails yet, consider doing so now and make sure to step-uptransactions if needed. Also, make sure to check out our guide on Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) if you are processing payments within the European Economic Area (EEA). Follow @GooglePayDevs on Twitter for future updates. If you have questions, mention @GooglePayDevs and include #AskGooglePayDevs in your tweets.
What's Your Reaction?